More Than Half of American-Owned IC Fab Capacity Exists Overseas
American IC manufacturers have 56% of their wafer capacity installed at fabs located in other regions of the world, according to the new Global Wafer Capacity 2023 report from Knometa Research. As of year-end 2022, American companies have installed capacity of 4.6 million 200mm-equivalent wafers per month, with 2.0 million in domestic fabs and 2.6 million in fabs at foreign sites.
Of the major IC producing countries and regions (Americas, China, Europe, Japan, Korea, and Taiwan), the Americas region is unique in that foreign capacity exceeds that of domestic capacity.
Of the major IC producing countries and regions (Americas, China, Europe, Japan, Korea, and Taiwan), the Americas region is unique in that foreign capacity exceeds that of domestic capacity.
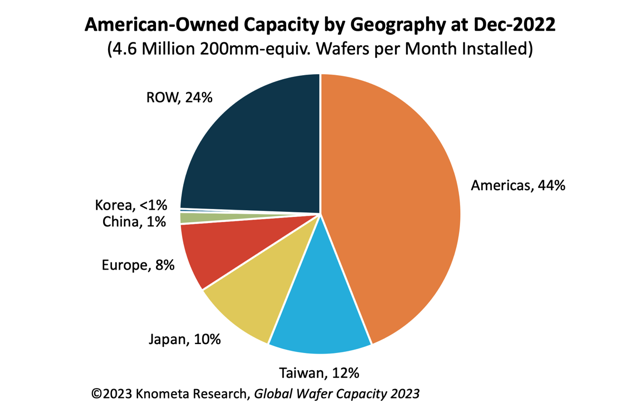
The biggest volumes of offshore capacity for American companies are in Singapore (22% share of total), Taiwan (12%), Japan (10%), Germany (4%), Ireland (3%), and Israel (2%).
With its many large fabs in Singapore, Taiwan, and Japan, Micron owns by far the most offshore capacity, accounting for 65% of the 2.6 million wafers in monthly capacity. GlobalFoundries is next with a 14% share followed by Intel with 9% and Texas Instruments with 5%.
In the past couple years, American companies have announced several major fab construction projects in the U.S. Some of these came about as a result of the CHIPS Act passed by the U.S. government in July 2022 to boost American semiconductor research, development, and manufacturing.
American-owned fabs under construction in the U.S. and scheduled to open during 2024-2025 include:
Micron will also build a large fab site in Clay, New York, but this project is part of the company's long-term capacity expansion plans and construction will not begin until 2024 at the earliest. In January 2023, Analog Devices announced plans to double the capacity of its fab in Beaverton, Oregon.
While the share of domestic IC wafer capacity will increase some in the next several years with the opening of these large new fabs in the U.S., American companies are building or have plans to build additional fabs at overseas sites as well. Moreover, Intel's pending acquisition of Tower Semiconductor, with its fabs in Israel and Japan (as well as the U.S.), will shift the balance in the direction of more foreign capacity. Had Tower been part of Intel at the end of 2022 with the headquarters of the combined operations being in the U.S., the foreign share of American-owned capacity would be one percentage point higher at 57%.
The Global Wafer Capacity 2023 report is available for purchase here.
- Singapore: Micron Technology - 4 fabs, GlobalFoundries - 4 fabs
- Taiwan: Micron Technology - 4 fabs, Diodes - 1 fab
- Japan: Micron Technology - 4 fabs, TI - 2 fabs, Onsemi - 1 fab
- Germany: GlobalFoundries - 2 fabs, TI - 1 fab
- Ireland: Intel - 1 fab, Analog Devices - 1 fab
- Israel: Intel - 2 fabs
With its many large fabs in Singapore, Taiwan, and Japan, Micron owns by far the most offshore capacity, accounting for 65% of the 2.6 million wafers in monthly capacity. GlobalFoundries is next with a 14% share followed by Intel with 9% and Texas Instruments with 5%.
In the past couple years, American companies have announced several major fab construction projects in the U.S. Some of these came about as a result of the CHIPS Act passed by the U.S. government in July 2022 to boost American semiconductor research, development, and manufacturing.
American-owned fabs under construction in the U.S. and scheduled to open during 2024-2025 include:
- Intel - Fabs 52 and 62 in Chandler, Arizona
- Texas Instruments - Fabs SM1 and SM2 in Sherman, Texas
- Intel - Fab 27 in New Albany, Ohio
- Micron - Fab in Boise, Idaho
Micron will also build a large fab site in Clay, New York, but this project is part of the company's long-term capacity expansion plans and construction will not begin until 2024 at the earliest. In January 2023, Analog Devices announced plans to double the capacity of its fab in Beaverton, Oregon.
While the share of domestic IC wafer capacity will increase some in the next several years with the opening of these large new fabs in the U.S., American companies are building or have plans to build additional fabs at overseas sites as well. Moreover, Intel's pending acquisition of Tower Semiconductor, with its fabs in Israel and Japan (as well as the U.S.), will shift the balance in the direction of more foreign capacity. Had Tower been part of Intel at the end of 2022 with the headquarters of the combined operations being in the U.S., the foreign share of American-owned capacity would be one percentage point higher at 57%.
The Global Wafer Capacity 2023 report is available for purchase here.